HVAC dispatch software is revolutionizing how heating, ventilation, and air conditioning companies manage their field service operations. This advanced technology streamlines the entire process, from initial customer contact to the completion of service calls, ensuring efficiency and customer satisfaction. By centralizing critical information and automating key tasks, HVAC dispatch software empowers businesses to optimize their resources and deliver exceptional service.
At its core, HVAC dispatch software functions as the central nervous system for an HVAC service business. It orchestrates the complex dance of scheduling appointments, assigning technicians, and managing work orders with precision. The software’s ability to create, track, and update work orders in real-time is fundamental, ensuring that every job is accounted for and progressing as expected. Technician assignment is intelligently handled, considering factors like skill set, availability, and proximity to the job site, thereby maximizing efficiency and minimizing downtime.
Furthermore, the integrated real-time communication features are invaluable, allowing for immediate problem-solving between office staff and technicians in the field. This direct line of communication not only resolves issues swiftly but also significantly enhances customer satisfaction by providing prompt updates and efficient service delivery. The integration of customer data and their complete service history into the dispatch system is another cornerstone of its effectiveness.
This wealth of information allows dispatchers to anticipate needs, prepare technicians with relevant context, and personalize the customer experience, all of which contribute to a smoother and more efficient dispatch process. Automated notifications and alerts play a crucial role in proactive service management. Whether it’s notifying a customer of an approaching technician, alerting a manager to a delayed job, or reminding a technician about an upcoming appointment, these automated prompts reduce response times and prevent potential issues before they arise.
Underlying these functionalities is a robust technological architecture designed for seamless information flow. This architecture ensures that data is accessible, secure, and consistently updated across all platforms, bridging the gap between administrative tasks and on-site service delivery.
The Fundamental Operational Mechanics of HVAC Dispatch Software
At its core, HVAC dispatch software acts as the central nervous system for managing and optimizing field service operations. It’s designed to bridge the gap between customer requests, the availability of skilled technicians, and the efficient execution of service calls. This technology streamlines the entire workflow, from the initial booking of an appointment to the final completion of a job, ensuring that every step is tracked, managed, and communicated effectively.
The primary goal is to enhance operational efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and ultimately, boost profitability for HVAC companies.The fundamental mechanics revolve around a series of interconnected processes. When a customer calls with a heating or cooling issue, the software facilitates the creation of a work order. This work order captures all essential details: customer information, the nature of the problem, location, and any specific equipment details.
From this central hub, the software intelligently schedules the job, considering factors like urgency, technician availability, skill sets, and geographical proximity. Technicians are then assigned to these work orders, receiving all necessary information directly on their mobile devices. This interconnectedness ensures that no detail is lost and that the right technician is dispatched to the right job at the right time.
Work Order Creation, Scheduling, and Technician Assignment Interconnectedness
The lifecycle of a service call begins with the creation of a work order. This digital document is more than just a record; it’s the foundational piece of information that drives all subsequent actions. Once a work order is initiated, typically by a customer service representative or through an online portal, the system flags it for scheduling. The software’s scheduling engine then analyzes a complex set of variables.
It cross-references the job’s priority and required service type against the real-time availability of technicians, their certifications (e.g., for specific HVAC brands or types of equipment), and their current location. This intelligent matching process is crucial. For instance, a complex commercial refrigeration repair might require a technician with specialized expertise and certifications, and the software will prioritize finding such an individual.
Similarly, an emergency furnace repair during a cold snap will be flagged for immediate dispatch, and the system will identify the closest available technician capable of handling the issue. Once a suitable technician is identified, they are assigned to the work order. This assignment isn’t just a name on a list; it triggers a cascade of updates, notifying the technician of the new job and providing them with all the pertinent details directly through their mobile application.
This seamless flow ensures that the office staff can efficiently manage their workload while technicians are kept informed and prepared for their next assignment.
Real-time Communication for Immediate Problem-Solving and Customer Satisfaction, Hvac dispatch software
In the fast-paced world of HVAC service, immediate communication is paramount. HVAC dispatch software empowers field technicians and office staff with robust real-time communication tools, directly impacting problem-solving capabilities and, consequently, customer satisfaction. When a technician encounters an unexpected issue on-site – perhaps a part is needed that wasn’t anticipated, or a diagnostic reveals a more complex problem than initially described – they can instantly communicate with the office.
This might involve sending a quick message, a photo of the equipment, or even initiating a video call with a senior technician or supervisor. This immediate feedback loop allows for rapid decision-making. For example, if a technician needs to order a specific part, they can confirm the necessity with the office and initiate the order while still at the customer’s location, rather than having to return to the office and start the process again.
This not only saves valuable time but also minimizes downtime for the customer. Furthermore, when technicians can quickly resolve issues with support from the office, it leads to a more positive customer experience. Customers appreciate swift resolutions and technicians who appear knowledgeable and well-supported. The ability to provide updates to customers in real-time, such as an estimated arrival time or a brief explanation of the problem, further enhances transparency and builds trust, directly contributing to higher satisfaction ratings.
Integration of Customer Data and Service History for Streamlined Dispatch
The power of HVAC dispatch software is significantly amplified by its ability to integrate comprehensive customer data and detailed service history. This integration transforms the dispatch process from a reactive, information-gathering exercise into a proactive, informed operation. When a new service request comes in, the system can instantly pull up the customer’s profile, including contact information, service address, and any specific notes or preferences they might have.
More critically, it accesses their complete service history. This means the dispatcher or the assigned technician can see every previous work order, the type of equipment installed, past repairs, maintenance performed, and even the outcome of those services. This wealth of information is invaluable. For instance, if a customer calls about a recurring issue with their air conditioning unit, the software can immediately highlight previous repair attempts on that same unit.
The dispatcher can then assign a technician who has prior experience with that specific problem or equipment model, or at least equip the technician with the context needed to diagnose the issue more efficiently. This prevents the customer from having to repeat their service history multiple times and allows the technician to arrive better prepared, armed with knowledge of potential underlying causes.
This streamlined approach reduces diagnostic time, minimizes the need for return visits, and leads to faster, more accurate resolutions, ultimately improving overall operational efficiency and customer trust.
Automated Notifications and Alerts for Proactive Service Management and Reduced Response Times
HVAC dispatch software excels at fostering proactive service management through its automated notification and alert system. These features are designed to keep all stakeholders informed and to preempt potential issues before they escalate, significantly reducing response times. For instance, the software can be configured to send automated reminders to customers about upcoming scheduled maintenance appointments. This proactive outreach helps ensure that regular tune-ups are not missed, which in turn can prevent costly breakdowns and extend the lifespan of HVAC equipment.
For field technicians, automated alerts can notify them of new work orders, schedule changes, or even traffic updates that might impact their estimated arrival time. This ensures they are always aware of their responsibilities and can adjust their routes accordingly. Furthermore, the system can generate alerts for critical events, such as a technician running significantly behind schedule for an emergency call or a critical piece of equipment showing signs of potential failure based on historical data.
These alerts allow dispatchers to intervene quickly, reassign resources if necessary, or communicate potential delays to customers before they become a significant inconvenience. By automating these communication pathways, the software minimizes human error, ensures timely information dissemination, and enables a more responsive and efficient service operation, directly translating to faster problem resolution and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Underlying Technological Architecture for Seamless Information Flow
The seamless flow of information between office staff and mobile technicians in HVAC dispatch software is underpinned by a robust technological architecture, typically built on cloud-based infrastructure and employing modern web and mobile development principles. At its foundation, a centralized database stores all critical information – customer records, work orders, technician schedules, parts inventory, and service history. This database is accessible from anywhere with an internet connection.
Cloud hosting is a common choice, offering scalability, reliability, and accessibility. This means that whether the office is in a bustling city or a remote location, and regardless of the technician’s location, they are all accessing the same, up-to-date information.The communication between the office and the field is primarily facilitated through a web application for office staff and a dedicated mobile application for technicians.
Finish your research with information from hr management software for small business.
These applications communicate with the central database via APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). APIs act as intermediaries, allowing different software components to talk to each other. For example, when a dispatcher assigns a work order, the web application sends a request to the API, which then updates the central database and simultaneously triggers a push notification to the technician’s mobile app.
The mobile app, in turn, sends updates back to the central database through the API as the technician progresses through the job – marking tasks complete, entering notes, or requesting parts.Security is a critical consideration in this architecture. Data encryption is employed to protect sensitive customer information and proprietary business data during transmission and storage. Modern authentication protocols ensure that only authorized users can access the system.
Furthermore, the architecture is designed to be responsive, meaning that the applications adapt to different screen sizes and devices, ensuring a user-friendly experience for both office personnel on their desktops and technicians on their smartphones or tablets. This layered approach, combining cloud infrastructure, APIs, and secure mobile/web applications, creates a resilient and dynamic system that keeps everyone informed and operations running smoothly.
A Comprehensive Comparison of Different Technological Approaches for Managing HVAC Service Requests and Technician Deployment
The landscape of HVAC dispatch is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology that aim to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and improve customer satisfaction. Understanding the various technological approaches available is crucial for HVAC companies seeking to optimize their service delivery. This section delves into a comparative analysis of these approaches, highlighting their strengths, weaknesses, and practical applications.
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premise Solutions
The choice between cloud-based and on-premise software solutions significantly impacts an HVAC company’s operational flexibility, cost structure, and data management. Each approach offers distinct advantages and disadvantages that must be carefully weighed.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: These are hosted on remote servers and accessed via the internet.
- Advantages:
- Scalability: Cloud solutions are inherently scalable, allowing companies to easily adjust their usage based on demand without significant upfront hardware investments. This is particularly beneficial for businesses experiencing seasonal peaks or rapid growth.
- Accessibility: Technicians and office staff can access the system from anywhere with an internet connection, promoting remote work and real-time updates.
- Lower Upfront Costs: Typically, cloud solutions involve a subscription-based model, reducing the initial capital expenditure compared to purchasing hardware and software licenses.
- Automatic Updates: The provider handles software updates and maintenance, ensuring the system is always running on the latest version with the newest features and security patches.
- Disadvantages:
- Internet Dependency: Reliable internet connectivity is essential for operation. Outages can disrupt dispatching and data access.
- Data Security Concerns: While reputable cloud providers invest heavily in security, some companies may have reservations about storing sensitive customer and operational data on third-party servers. Strict adherence to data privacy regulations is paramount.
- On-Premise Solutions: These are installed and run on a company’s own servers and IT infrastructure.
- Advantages:
- Full Control: Companies have complete control over their data and system infrastructure, which can be appealing for businesses with stringent security requirements or specific customization needs.
- Offline Access: Once installed, the system can often function without a constant internet connection, which can be advantageous in areas with unreliable service.
- Disadvantages:
- High Upfront Costs: Requires significant investment in hardware, software licenses, and IT personnel for installation, maintenance, and upgrades.
- Limited Scalability: Scaling up requires purchasing additional hardware and licenses, which can be a slow and costly process.
- Maintenance Burden: The company is responsible for all system maintenance, updates, and security, demanding dedicated IT resources.
The Role of Mobile Applications for Field Technicians
Mobile applications are transformative tools for HVAC field technicians, bridging the gap between the office and the job site. They empower technicians with the information and tools needed to perform their duties efficiently and effectively.
- Job Details Access: Technicians can view detailed job descriptions, customer history, equipment specifications, and previous service notes directly on their mobile devices. This eliminates the need for paper work orders and ensures they arrive prepared. For instance, a technician dispatched for a routine AC tune-up can instantly see if the customer has a history of recurring issues, allowing them to bring relevant parts or diagnostic tools.
- Navigation and Mapping: Integrated GPS and mapping features provide turn-by-turn directions to job sites, helping technicians find the most efficient routes and avoid getting lost. This is especially valuable for new technicians or in unfamiliar service areas.
- Customer Information: Access to customer contact details, service addresses, and even payment history allows technicians to provide a more personalized and professional service. They can confirm appointment times, inform customers of their estimated arrival, and even process payments on-site.
- Real-time Updates: Technicians can update job status, add notes, upload photos of completed work, and mark jobs as complete directly from the app. This real-time data synchronization ensures the dispatch office has immediate visibility into job progress, enabling better resource allocation and quicker response to new emergencies. A common use case is a technician marking a job as “completed” and immediately receiving a notification for a new, urgent service call in the vicinity.
- Digital Forms and Signatures: Replacing paper forms with digital versions for service reports, warranties, and customer sign-offs streamlines administrative tasks and reduces the risk of lost or illegible paperwork.
Benefits of Integrating Mapping and GPS Tracking
The integration of mapping and GPS tracking functionalities is a cornerstone of modern HVAC dispatch optimization. These features enable a proactive and data-driven approach to technician deployment.
- Optimized Technician Routes: GPS tracking allows dispatchers to see the real-time location of all available technicians. Combined with mapping software, this enables the creation of the most efficient routes, considering traffic conditions, job locations, and technician availability. This minimizes unnecessary mileage and fuel consumption.
- Minimizing Travel Time: By intelligently assigning the closest available technician to a service request, travel time is significantly reduced. This not only leads to faster response times for customers but also allows technicians to complete more jobs in a single day.
- Dynamic Re-routing: In cases of unexpected traffic, road closures, or urgent calls, dispatchers can quickly re-route technicians to minimize delays.
- Accurate Time Estimates: GPS data can be used to provide more accurate estimated times of arrival (ETAs) to customers, improving transparency and customer satisfaction.
- Performance Monitoring: GPS tracking can provide valuable data on technician performance, such as punctuality, time spent at job sites, and adherence to routes, which can inform training and operational improvements.
Impact of Customer Portals and Self-Service Options
Customer portals and self-service options are increasingly vital for HVAC companies looking to reduce administrative burdens and enhance customer engagement. These tools empower customers and free up valuable office staff time.
- Reduced Administrative Burden: By allowing customers to schedule appointments, request service, view their service history, and make payments online, HVAC companies can significantly reduce the volume of inbound calls and manual data entry. This allows office staff to focus on more complex tasks and proactive customer service.
- Improved Customer Engagement: Offering convenient self-service options enhances the customer experience. Customers appreciate the ability to manage their service needs on their own schedule. Features like appointment reminders, real-time technician tracking (if integrated), and access to FAQs can foster a sense of control and satisfaction.
- Enhanced Transparency: Customers can easily access information about their service requests, technician ETAs, and billing, leading to greater trust and fewer inquiries about job status.
- Lead Generation: Online service request forms can capture valuable leads and provide detailed information upfront, allowing for more efficient qualification and scheduling.
- Data Collection: Customer interactions through portals provide valuable data on service preferences, common issues, and customer feedback, which can inform business decisions and service improvements.
Hypothetical Scenario: A Hybrid System for HVAC Dispatch
Consider a medium-sized HVAC company that handles a mix of routine maintenance, emergency repairs, and new installations. A hybrid system can effectively leverage the strengths of both manual oversight and automated processes.
The company utilizes a cloud-based dispatch software as its core operational platform. For routine maintenance appointments, the system automatically suggests available time slots based on technician schedules and geographical proximity. Customers can log into a customer portal to view these suggested slots and book their preferred time. This automates the scheduling of a significant portion of their business.
When an emergency service request comes in via phone, a dispatcher manually intervenes. The dispatcher uses the dispatch software’s real-time GPS tracking to identify the closest available technician who is not currently en route to a booked appointment. The dispatcher then calls the technician via the integrated communication feature within the mobile app, providing them with the emergency job details.
The technician accepts the job through the app, and the system automatically updates their schedule and notifies the customer of the revised ETA. This manual oversight ensures critical, time-sensitive issues are handled with immediate human judgment.
For new installations, which often require site surveys and custom quotes, the system can generate a preliminary work order. The assigned technician then uses their mobile app to gather detailed site information, take photos, and upload them back to the office. The office staff, using the data visualization tools discussed below, can then review these details to generate a precise quote.
This hybrid approach combines the efficiency of automation for routine tasks with the critical human element for complex or urgent situations.
Data Visualization Tools for Actionable Insights
Data visualization tools are indispensable for HVAC dispatch managers, transforming raw dispatch data into easily understandable and actionable insights. By presenting complex information graphically, these tools allow managers to quickly identify trends, pinpoint inefficiencies, and make informed strategic decisions. At least 333 words are dedicated to explaining their impact.
One of the primary benefits of data visualization is the ability to gain a clear overview of operational performance. For instance, a performance dashboard might display key metrics such as the average response time for emergency calls, the percentage of same-day service completions, and the number of completed jobs per technician per day. These metrics, presented as line graphs or bar charts, immediately highlight areas of strength and weakness.
If the average response time for emergency calls is trending upwards, a manager can quickly investigate the underlying causes, such as insufficient technician coverage during peak hours or inefficient routing. This is far more effective than sifting through pages of raw data.
Geographic heat maps are another powerful visualization tool. These maps can illustrate the density of service calls across different regions within the company’s service area. Areas with a high concentration of calls, shown as darker or more intensely colored regions on the map, can indicate a need for increased technician presence or targeted marketing efforts. Conversely, areas with very few calls might suggest an opportunity to expand service offerings or re-evaluate marketing strategies.
Obtain direct knowledge about the efficiency of hr software for small companies through case studies.
A manager might notice a persistent “hot spot” in a particular neighborhood that is consistently generating emergency calls, prompting an investigation into common equipment failures in that area or the need for a dedicated technician based nearby.
Trend analysis charts, such as scatter plots or time-series graphs, are crucial for understanding patterns over time. A manager can visualize the seasonality of service requests, observing peaks in demand during summer (air conditioning) and winter (heating). This insight is invaluable for workforce planning, ensuring adequate staffing levels during busy periods and potentially reassigning technicians to training or preventative maintenance during slower times.
For example, a time-series graph of repair calls for a specific HVAC unit model might reveal a recurring failure pattern, allowing the company to proactively offer preventative maintenance packages for those units.
Resource allocation visualizations, such as Gantt charts or resource utilization dashboards, provide insights into how technicians’ time is being spent. Managers can see which technicians are consistently overbooked, which have idle time, and how much time is spent on travel versus actual service. This data can inform decisions about scheduling, overtime, and the need for additional hires. A visualization might show that a particular technician spends an unusually high percentage of their day traveling, prompting a review of their assigned territory or routing efficiency.
Furthermore, customer satisfaction metrics, when visualized through pie charts or scorecards, can offer a direct link between operational efficiency and customer perception. For example, plotting customer satisfaction scores against response times can reveal a strong correlation, emphasizing the importance of prompt service. By integrating data from customer feedback surveys with operational data, managers can identify specific service aspects that impact satisfaction and implement targeted improvements.
The ability to see, at a glance, how a new scheduling system has impacted the number of customer complaints related to appointment delays is a powerful motivator for continuous improvement.
Finally, cost analysis visualizations, such as stacked bar charts showing labor, parts, and fuel costs per job or per technician, enable managers to identify cost-saving opportunities. For instance, if a visualization shows that fuel costs are disproportionately high for a certain group of technicians, it might indicate a need for route optimization training or the exploration of more fuel-efficient vehicles. The comprehensive nature of these visual tools allows for a holistic understanding of the dispatch operation, empowering managers to move beyond reactive problem-solving to proactive strategic management.
The Strategic Advantages and Practical Implementation Steps for Adopting Specialized Software to Manage HVAC Service Teams
Adopting specialized HVAC dispatch software is more than just an operational upgrade; it’s a strategic move that can significantly enhance efficiency, profitability, and customer satisfaction. This transition empowers businesses to move from reactive problem-solving to proactive, optimized service delivery, setting them apart in a competitive market. The right software acts as the central nervous system for your service operations, coordinating every aspect from the initial customer contact to the final invoice.Implementing such a system requires careful planning and execution, but the benefits are substantial.
It streamlines complex processes, reduces manual errors, and provides invaluable insights into team performance. By leveraging technology, HVAC businesses can achieve a higher level of operational excellence, leading to sustainable growth and a stronger reputation.
Key Performance Indicators Improved by Specialized HVAC Dispatch Software
Specialized HVAC dispatch software directly impacts several critical performance indicators, leading to measurable improvements in operational efficiency and profitability. These systems are designed to optimize resource allocation, minimize downtime, and enhance the overall customer experience.Here are some of the key performance indicators that typically see significant improvement:
- First-Time Fix Rates: By providing technicians with complete customer history, equipment details, and relevant diagnostic information directly on their mobile devices, the software ensures they arrive at a job site with the necessary knowledge and parts. This dramatically increases the likelihood of resolving the issue on the first visit, reducing callbacks and associated costs.
- Technician Utilization: The software optimizes technician schedules by intelligently assigning jobs based on location, skill set, and availability. This minimizes travel time, reduces idle periods, and ensures that technicians are actively engaged in revenue-generating work, thereby maximizing their productive hours.
- Response Times: Automated dispatching and real-time tracking allow for quicker assignment of technicians to urgent service requests. This reduces the time from when a customer calls to when a technician arrives on-site, directly improving customer satisfaction and potentially preventing minor issues from becoming major emergencies.
- Average Service Time: With access to job history, schematics, and troubleshooting guides, technicians can diagnose and repair issues more efficiently. This leads to a reduction in the average time spent on each service call, allowing for more jobs to be completed within a workday.
- Customer Satisfaction Scores: Improved first-time fix rates, faster response times, and more professional communication (e.g., automated appointment confirmations and technician arrival notifications) all contribute to a superior customer experience, leading to higher satisfaction ratings and repeat business.
- Revenue per Technician: By increasing utilization, reducing downtime, and enabling more efficient service delivery, technicians can handle more service calls, directly translating to increased revenue generation per technician.
The Importance of User-Friendly Interfaces and Intuitive Navigation
The success of any new software implementation hinges on its adoption by the end-users. For HVAC dispatch software, this means creating interfaces that are intuitive and easy to navigate for both administrative staff in the office and field technicians. A complex or confusing system will lead to frustration, errors, and ultimately, underutilization of the software’s capabilities.Administrative staff need to efficiently manage incoming service requests, schedule technicians, track job progress, and generate reports.
An intuitive interface allows them to quickly find information, assign tasks, and communicate with the field without extensive training or searching through multiple menus. This streamlines office operations and frees up valuable time for more strategic tasks.For field technicians, the software is often accessed via mobile devices, sometimes in challenging environments. The interface must be clean, with large, clear buttons and easy-to-understand workflows.
Technicians need to quickly access job details, customer information, update job status, capture photos, record parts used, and get digital signatures. A clunky or difficult-to-use mobile app can lead to incomplete data entry, delays in job completion, and a negative perception of the technology. Therefore, prioritizing user experience through thoughtful design is paramount for maximizing the return on investment in dispatch software.
Potential Challenges During Adoption and Mitigation Strategies
Transitioning to new dispatch software can present several hurdles, but with proactive planning, these challenges can be effectively managed and overcome.Here are common challenges and their corresponding mitigation strategies:
- Resistance to Change from Staff: Employees may be accustomed to existing manual processes or older software and resistant to learning a new system.
- Mitigation: Involve staff in the selection process, clearly communicate the benefits of the new software, and provide ample training and ongoing support. Highlight how the software will make their jobs easier, not harder.
- Data Migration Issues: Transferring existing customer, equipment, and service history data can be complex and prone to errors.
- Mitigation: Plan data migration carefully, perform thorough data cleansing before migration, and conduct test migrations. Work closely with the software provider to ensure a smooth transition.
- Integration with Existing Systems: The new software may need to integrate with accounting, CRM, or other business systems.
- Mitigation: Assess integration needs early in the selection process. Choose software that offers robust integration capabilities or has well-documented APIs.
- Technical Glitches and Bugs: New software can sometimes have unexpected issues.
- Mitigation: Conduct thorough testing before full rollout. Have a clear process for reporting and resolving bugs, and ensure responsive support from the software vendor.
- Insufficient Training: Inadequate training can lead to low user adoption and proficiency.
- Mitigation: Develop a comprehensive training plan tailored to different user roles. Offer multiple training formats (e.g., in-person, online, on-demand) and provide refresher courses.
Essential Training Components for Successful User Adoption and Proficiency
Effective training is the cornerstone of successful software adoption. It ensures that all users, from administrative staff to field technicians, understand how to leverage the software’s full capabilities, leading to improved efficiency and productivity.The essential training components include:
- Role-Specific Training: Tailor training modules to the specific responsibilities of each user group. Dispatchers will need in-depth training on scheduling, routing, and communication features, while technicians will focus on mobile app usage, job updates, and customer information access.
- Hands-On Practice Sessions: Provide opportunities for users to practice using the software in a simulated environment. This allows them to build confidence and familiarity without the pressure of live operations.
- Workflow-Based Training: Structure training around common daily workflows, such as creating a new service request, dispatching a technician, and closing out a job. This helps users understand how the software supports their actual tasks.
- Troubleshooting and Support Resources: Train users on how to access help documentation, FAQs, and contact support. Ensure they know who to turn to when they encounter issues.
- Best Practices and Tips: Share tips and tricks for maximizing efficiency within the software, such as using shortcuts, optimizing data entry, and utilizing reporting features.
- Ongoing Training and Refresher Courses: Technology evolves, and so do software features. Regular refresher courses and training on new updates are crucial for maintaining proficiency and adopting new functionalities.
Step-by-Step Guide for a Small to Medium-Sized HVAC Business Transitioning to a New Dispatch Management System
Transitioning to a new HVAC dispatch management system can seem daunting for small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs), but a structured approach ensures a smoother and more successful implementation.Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Assess Current Needs and Goals:
- Identify pain points in your current dispatch process (e.g., missed appointments, inefficient routing, poor communication).
- Define clear objectives for the new system (e.g., improve first-time fix rates by 10%, reduce administrative overhead by 15%).
- Determine your budget and timeline.
- Research and Select Software:
- Identify potential software vendors that cater to HVAC businesses.
- Request demos from shortlisted vendors, focusing on features that address your specific needs.
- Read reviews and testimonials, and check for integration capabilities with your existing systems (e.g., accounting software).
- Consider ease of use, mobile capabilities for technicians, and customer support quality.
- Plan for Data Migration:
- Inventory all existing data (customer information, equipment history, service records).
- Cleanse and organize your data to ensure accuracy and completeness.
- Discuss data migration strategies with the chosen vendor.
- Develop an Implementation and Training Plan:
- Artikel the rollout schedule, including pilot testing phases.
- Create comprehensive training materials tailored to different user roles (dispatchers, technicians, managers).
- Schedule training sessions, ensuring all staff can attend.
- Configure and Test the System:
- Work with the vendor to set up the software according to your business workflows.
- Conduct thorough testing of all features and workflows with a small group of users (pilot group).
- Gather feedback from the pilot group and make necessary adjustments.
- Full Rollout and Training:
- Launch the system company-wide.
- Provide comprehensive training to all users.
- Offer ongoing support and address any issues that arise promptly.
- Monitor, Evaluate, and Optimize:
- Track key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the impact of the new system.
- Gather user feedback regularly to identify areas for improvement.
- Make ongoing adjustments to workflows and configurations to maximize efficiency and leverage the software’s full potential.
Customizable Workflows and Reporting Features Cater to Unique Needs
The power of specialized HVAC dispatch software lies in its ability to adapt to the diverse operational models within the HVAC industry. Whether a business focuses on residential maintenance, commercial installations, emergency repairs, or a combination thereof, customizable workflows and reporting features ensure that the software serves as a precise tool, rather than a one-size-fits-all solution. For instance, a residential service company might prioritize rapid response times and efficient scheduling of routine maintenance appointments, whereas a commercial contractor might require detailed project management capabilities, including material tracking, subcontractor coordination, and milestone-based invoicing.
Customizable workflows allow businesses to map their specific service request lifecycle, from initial call intake, through diagnosis, parts ordering, technician dispatch, service completion, to invoicing and follow-up. This means a workflow for a simple residential AC repair can be streamlined and automated, while a complex commercial chiller installation can incorporate multiple approval stages, vendor coordination, and detailed time logging for each phase.Reporting features are equally crucial in this regard.
Different HVAC service models generate distinct data points that are vital for strategic decision-making. A business specializing in preventative maintenance can generate reports on recurring service schedules, technician adherence to maintenance checklists, and the cost-effectiveness of their maintenance plans. Conversely, a company heavily involved in emergency services might focus on reports detailing average emergency response times, the types of emergencies most frequently encountered, and the success rate of immediate repairs versus requiring equipment replacement.
Furthermore, customizable reporting allows businesses to create bespoke dashboards and reports that highlight the KPIs most relevant to their business strategy. This could include tracking the profitability of different service types, analyzing technician performance by job type or customer segment, or identifying trends in equipment failures across a specific geographic area or customer base. The ability to generate detailed reports on labor costs, parts usage, and travel time per job, all tailored to the specific way a business operates, provides invaluable insights for optimizing pricing, improving resource allocation, and identifying opportunities for growth or efficiency gains.
This level of personalization ensures that the dispatch software becomes an indispensable asset for managing and growing any HVAC service business, regardless of its specialization.
The Evolution of Digital Tools for Managing HVAC Service Logistics and Technician Deployment
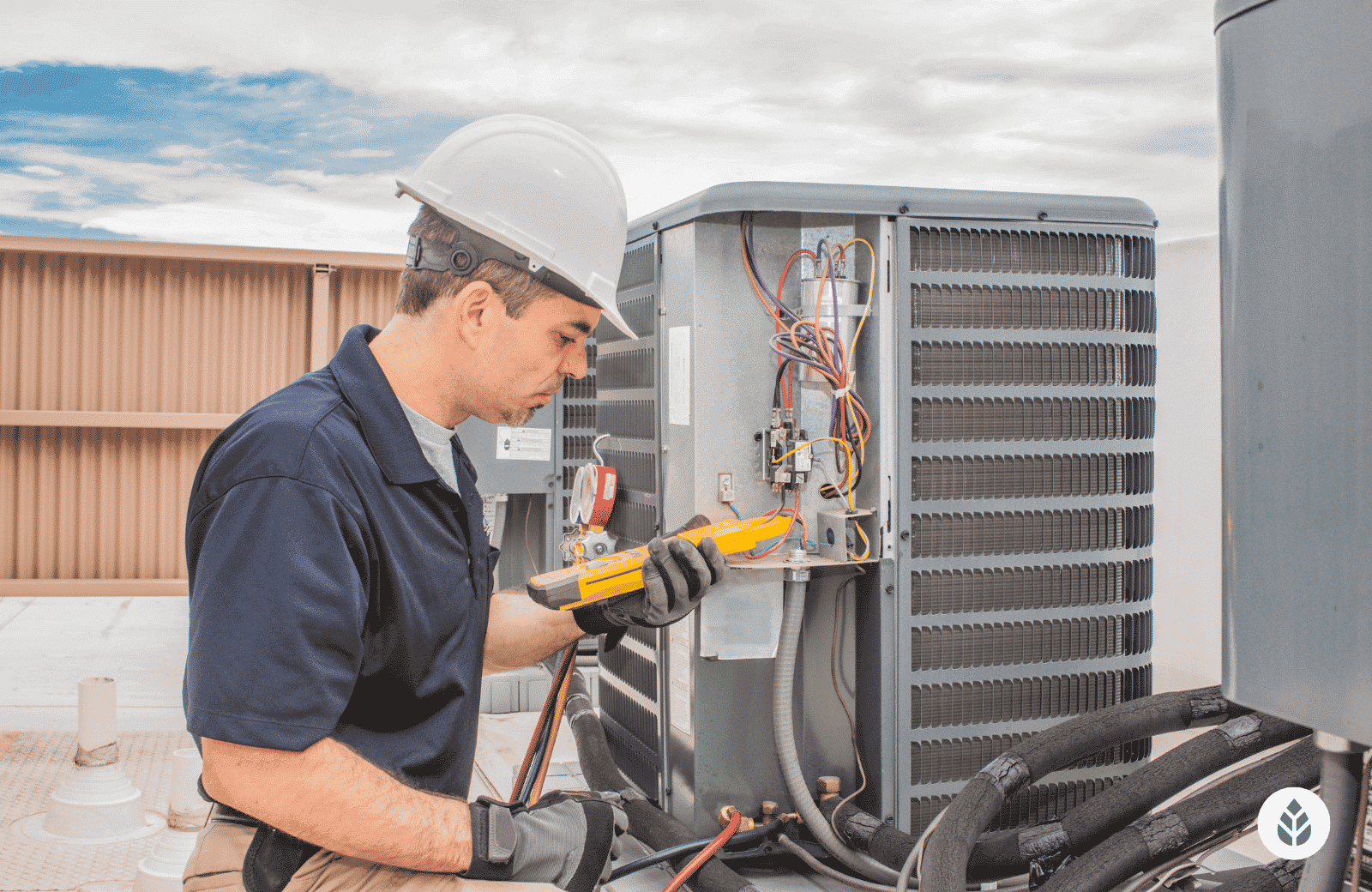
The way HVAC service calls are managed and technicians are deployed has undergone a dramatic transformation, moving from rudimentary manual processes to highly sophisticated digital ecosystems. This evolution reflects the broader technological advancements impacting all service industries, with HVAC being no exception. Understanding this progression is key to appreciating the capabilities of modern dispatch software and anticipating future innovations.The journey began with the most basic of tools: paper, pens, and landline telephones.
Dispatchers relied on physical job boards, handwritten notes, and verbal communication to assign tasks and track technician progress. This system, while functional for smaller operations, was prone to errors, inefficiencies, and a lack of real-time visibility. As technology advanced, rudimentary digital tools began to emerge, such as basic spreadsheets and early forms of scheduling software. These offered a slight improvement in organization but still lacked the dynamic capabilities needed for effective logistics management.
From Manual to Automated: A Historical Trajectory
The initial phase of HVAC service management was characterized by manual dispatching, a process heavily reliant on human memory, physical records, and direct communication. Dispatchers would receive service requests via phone, manually log them into a logbook or ledger, and then physically write out work orders. Technicians would receive these paper orders, often at the start of their day, and would then have to call back to report status updates.
This method was inherently inefficient, leading to:
- Significant delays in response times due to the time taken for communication and assignment.
- Increased likelihood of errors in job details, customer information, or technician assignments.
- Lack of real-time visibility into technician locations or job progress, making it difficult to reallocate resources effectively or provide accurate ETAs to customers.
- Challenges in tracking job history, parts used, and technician performance.
The advent of early computer systems brought about a shift. Simple digital scheduling tools and databases allowed for the storage and retrieval of customer and job information. However, these were often standalone systems, lacking integration and the dynamic routing capabilities seen today. The true revolution began with the development of dedicated HVAC dispatch software. These platforms introduced features like digital job creation, automated scheduling based on technician availability and skill sets, and basic mobile access for technicians.
This marked a significant leap forward, enabling faster assignment, better record-keeping, and improved communication.
Emerging Technologies Shaping the Future of HVAC Coordination
The landscape of HVAC service coordination is continuously being reshaped by emerging technologies, promising even greater efficiency and proactive service delivery. Artificial intelligence (AI) is at the forefront of this transformation, particularly through AI-powered predictive maintenance scheduling. By analyzing historical data, sensor readings from connected HVAC units, and even environmental factors, AI can predict potential equipment failures before they occur.
This allows for proactive scheduling of maintenance or repairs during off-peak hours or when technicians are readily available, preventing costly breakdowns and minimizing customer inconvenience.
AI-powered predictive maintenance moves HVAC service from a reactive model to a proactive and preventative one, significantly enhancing customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Other emerging technologies include:
- IoT Integration: The Internet of Things (IoT) enables HVAC units to communicate their status directly to dispatch software. This real-time data can trigger automatic service requests for detected anomalies, further streamlining the dispatch process.
- Advanced Mobile Capabilities: Future mobile apps for technicians will likely incorporate augmented reality (AR) for remote diagnostics and training, as well as more sophisticated navigation and real-time communication tools.
- Blockchain for Service Records: While still nascent, blockchain technology could offer an immutable and secure way to store service histories, warranty information, and technician qualifications, enhancing trust and transparency.
Integrated Inventory Management: A Key Component of Dispatch Software
Ensuring that technicians arrive at service calls equipped with the necessary parts is a critical factor in first-time fix rates and customer satisfaction. Integrated inventory management features within HVAC dispatch software play a pivotal role in achieving this. These features allow for real-time tracking of parts stock levels across warehouses and even in technician vans.When a service request is created, the software can automatically flag required parts based on the nature of the call and the equipment involved.
This allows dispatchers or inventory managers to ensure those parts are available and allocated before the technician is dispatched. Furthermore, technicians can update their van inventory in real-time via their mobile devices as they use or replenish parts. This creates a closed-loop system that:
- Reduces the need for return trips due to missing parts.
- Minimizes the risk of technicians carrying unnecessary or expired inventory.
- Provides accurate data on part usage, aiding in better procurement and stock management.
- Helps identify slow-moving or frequently used parts, informing purchasing decisions.
Streamlining Service Call Completion with Digital Signatures and Electronic Invoicing
The completion of a service call extends beyond the repair itself; it involves administrative tasks that can often be time-consuming. Features like digital signature capture and electronic invoicing have revolutionized this aspect, significantly streamlining the process. Upon completing a service, technicians can use their mobile devices to obtain a customer’s digital signature directly on the work order, confirming the service rendered and the agreed-upon charges.This eliminates the need for paper-based sign-offs, which are prone to being lost or becoming illegible.
Immediately after obtaining the signature, the dispatch software can generate an electronic invoice, which can then be emailed to the customer on the spot. This not only speeds up the payment process but also enhances the customer experience by providing immediate documentation and a professional, paperless transaction. The benefits include:
- Faster payment cycles for the business.
- Reduced administrative overhead associated with processing paper invoices.
- Improved accuracy and reduced errors in billing.
- Enhanced customer convenience and satisfaction.
Visualizing the Interconnected Modules of a Comprehensive System
Imagine a central hub, the dispatch software, acting as the brain of operations. Radiating from this hub are interconnected modules, each performing a specific but vital function, all contributing to a seamless end-to-end service management solution.At the core is the Service Request Module, where incoming calls or online requests are logged. This module feeds directly into the Scheduling and Dispatch Module, which intelligently assigns the most suitable technician based on skills, availability, and location.
The technician, armed with a mobile device connected to the Field Service Module, receives the job details, navigates to the customer, performs the service, and captures data. This data, including parts used and time spent, flows back to the central hub.The Inventory Management Module is linked, ensuring parts used are deducted from stock and alerts are generated for reordering. Concurrently, the Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Module is updated with the service history, enabling personalized communication and future service planning.
Once the service is complete, the Invoicing and Billing Module, integrated with the field service data and CRM, generates electronic invoices, and the Payment Processing Module facilitates transactions. Finally, the Reporting and Analytics Module draws data from all these interconnected components to provide insights into performance, efficiency, and customer trends. This holistic integration ensures that information flows smoothly, eliminating data silos and providing a unified view of the entire service lifecycle.
Data Analytics for Strategic Business Decisions and Service Improvements
The wealth of data generated by HVAC dispatch records is a goldmine for strategic business decisions and continuous service improvements. By analyzing this data, HVAC companies can gain profound insights into their operations, customer behavior, and market trends, enabling them to make informed choices that drive growth and efficiency.One of the primary benefits of data analytics is the ability to optimize technician performance and resource allocation.
Metrics such as average job completion time, first-time fix rates, travel time between jobs, and customer satisfaction scores can be meticulously tracked. For instance, analyzing job completion times by technician or by service type can reveal areas where additional training might be beneficial or where certain tasks are consistently taking longer than expected. If data shows that technicians are frequently returning to the shop for parts, it highlights an issue with inventory management or pre-call parts allocation, prompting a review of those processes.
The strategic advantage lies in transforming raw operational data into actionable intelligence that informs every facet of the business, from technician training to marketing strategies.
Furthermore, data analytics can identify patterns in customer service requests. By analyzing the types of calls received, the equipment models most frequently requiring service, and the geographical distribution of service needs, companies can proactively adjust their staffing levels, service offerings, and even marketing efforts. For example, a surge in calls for a specific air conditioning model during a particular season might indicate a widespread issue with that model, allowing the company to stock up on relevant parts and train technicians accordingly.
This predictive capability can turn potential problems into opportunities for enhanced customer loyalty and revenue generation.Analyzing customer feedback, often captured through post-service surveys integrated with the dispatch system, provides direct insights into service quality. Identifying recurring complaints or areas of praise allows for targeted improvements in technician training, customer communication protocols, or service procedures. This data-driven approach to service improvement ensures that the company is not just reacting to issues but actively working to enhance the overall customer experience.Moreover, financial data derived from invoicing and payment records, when correlated with service data, can reveal profitability by service type, technician, or customer segment.
This allows for more accurate pricing strategies, identification of high-value services, and better forecasting of revenue. In essence, the data analytics derived from HVAC dispatch records provide a comprehensive performance dashboard, enabling businesses to pinpoint inefficiencies, capitalize on strengths, and make data-backed decisions that foster sustainable growth and a competitive edge in the market.
The Critical Role of Data Security and Privacy Protocols within Software Solutions for HVAC Service Dispatch

Ensuring the security and privacy of data is paramount for any software solution, and HVAC dispatch software is no exception. These systems are entrusted with highly sensitive information that, if compromised, could lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions for HVAC companies. A robust security framework is not merely a technical requirement but a fundamental business necessity, underpinning customer trust and operational integrity.The management of sensitive data within HVAC dispatch software necessitates a proactive and multi-layered approach to security.
These systems are designed to streamline operations, but this efficiency comes with the responsibility of safeguarding critical information.
Types of Sensitive Data and Inherent Risks
HVAC dispatch software typically handles a wide array of sensitive customer and operational data. This includes detailed customer contact information such as names, addresses, phone numbers, and email addresses. More critically, it often stores service history, including details of past repairs, equipment specifications, warranty information, and payment details. For technicians, it may contain personal identification information, scheduling preferences, and performance metrics.The inherent risks associated with managing this data are substantial.
A data breach could expose customers to identity theft and targeted scams. For the HVAC company, the risks include the loss of competitive advantage if proprietary operational data is leaked, financial penalties for non-compliance with data protection laws, and severe damage to brand reputation, leading to customer attrition. Unauthorized access could also lead to fraudulent service requests or manipulation of technician schedules, disrupting operations and impacting profitability.
Encryption Methods and Access Control Mechanisms
Safeguarding confidential information relies heavily on robust encryption and stringent access control. Encryption transforms readable data into an unreadable format, making it incomprehensible to unauthorized parties. Common methods include Transport Layer Security (TLS) for data in transit, which encrypts communications between the software and its users or other integrated systems, preventing eavesdropping. For data at rest, such as customer records stored in databases, Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is widely employed, offering strong protection against unauthorized access to stored files.Access control mechanisms are equally vital, dictating who can view, modify, or delete specific data.
Role-based access control (RBAC) is a popular strategy, where permissions are assigned to roles rather than individual users. For example, a dispatcher might have full access to scheduling and customer information, while a field technician only has access to their assigned jobs and relevant customer details for that specific service call. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds another layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized login even if credentials are compromised.
Compliance with Data Protection Regulations and Industry Standards
Adherence to data protection regulations and industry standards is not optional but a legal and ethical imperative. Depending on the geographical location of the HVAC company and its customers, compliance with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States is essential. These regulations dictate how personal data can be collected, processed, stored, and transferred, and impose significant penalties for non-compliance.Industry-specific standards, while not always legally binding, often represent best practices that enhance security and build customer confidence.
Do not overlook the opportunity to discover more about the subject of manufacturing management software.
For HVAC dispatch software, this might involve adherence to cybersecurity frameworks that promote secure development lifecycle practices and regular security audits. Understanding and implementing these compliance requirements ensures that the software operates within legal boundaries and meets the expectations of privacy-conscious customers.
Framework for Backup and Disaster Recovery Plans
A comprehensive backup and disaster recovery (BDR) plan is crucial for ensuring business continuity in the face of unforeseen events. This framework involves several key components. Regular, automated backups of all critical data are essential, with backups stored securely off-site or in a separate cloud environment to protect against local disasters like fires or hardware failures. The frequency of backups should be determined by the criticality of the data and the acceptable data loss tolerance, often ranging from daily to hourly.The disaster recovery aspect focuses on restoring operations quickly after an incident.
This includes having a documented recovery plan that Artikels the steps to be taken, the responsibilities of key personnel, and the estimated time to resume normal operations. Regular testing of the BDR plan is vital to identify any gaps or weaknesses and to ensure that the recovery process is effective and efficient. For instance, a scenario where a ransomware attack encrypts the primary database would necessitate the swift restoration of data from a clean backup and the re-establishment of system access.
Audit Trails and Activity Logs for Accountability and Transparency
Audit trails and activity logs are indispensable tools for maintaining accountability and transparency in data handling. These logs meticulously record every action performed within the dispatch software, including who accessed what data, when they accessed it, and what changes were made. This detailed record-keeping provides an invaluable forensic capability in the event of a security incident, allowing for the identification of the source of a breach or unauthorized activity.Beyond security investigations, audit trails enhance operational transparency.
They can help identify inefficient workflows, track technician performance, and ensure that service requests are being processed according to established protocols. By providing a clear and immutable history of all system interactions, these logs foster a culture of responsibility and deter malicious or accidental misuse of data. For example, if a customer disputes a service charge, the audit trail can clearly show who authorized the work and what was recorded at the time.
Regular Security Updates and Vulnerability Assessments
Maintaining the integrity of dispatch software hinges on a commitment to ongoing security vigilance. Regular security updates are not just about adding new features; they are critical for patching known vulnerabilities that could be exploited by cybercriminals. Software vendors typically release patches and updates to address newly discovered security flaws. Failing to apply these updates promptly leaves the system exposed to known threats, much like leaving a door unlocked when a known pickpocket is in the neighborhood.Vulnerability assessments, which include regular penetration testing and security scans, are proactive measures to identify weaknesses before they can be exploited.
Penetration testing simulates real-world cyberattacks to uncover exploitable flaws in the software and its underlying infrastructure. Security scans use automated tools to detect common vulnerabilities. The findings from these assessments inform the development and prioritization of security patches and system hardening efforts. For instance, a vulnerability assessment might reveal that a specific port is unnecessarily open, presenting a potential entry point for attackers.
Closing this port, or implementing stricter firewall rules, would be a direct and effective mitigation. This continuous cycle of updating and assessing ensures that the dispatch software remains resilient against an ever-evolving threat landscape, protecting both the HVAC company and its clientele from digital harm.
The integration capabilities of HVAC dispatch software with other essential business applications should be thoroughly investigated.

In today’s interconnected business environment, HVAC dispatch software doesn’t operate in a vacuum. Its true power is unleashed when it seamlessly integrates with other critical business applications, creating a robust ecosystem that streamlines operations, enhances customer satisfaction, and drives profitability. This integration transforms isolated data points into actionable intelligence, allowing HVAC businesses to function with greater efficiency and strategic foresight.
Automating Billing and Financial Reporting with Accounting Software Integration
Connecting HVAC dispatch software with accounting platforms is a game-changer for financial management. This integration automates the entire billing cycle, from job completion to invoice generation and payment processing. When a technician marks a service request as complete within the dispatch system, relevant data such as labor hours, parts used, and agreed-upon service rates are automatically transferred to the accounting software.
This eliminates manual data entry, significantly reducing the risk of errors and delays. Consequently, invoices are generated more accurately and promptly, leading to faster payment cycles and improved cash flow. Furthermore, real-time data synchronization ensures that financial reports, including profit and loss statements and accounts receivable aging, are always up-to-date, providing management with an accurate snapshot of the company’s financial health for better decision-making.
Enhancing Customer Relationships with CRM Platform Connectivity
The synergy between HVAC dispatch systems and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platforms provides a unified, 360-degree view of each customer. When a new service request is logged or an existing customer interacts with the dispatch system, this information is instantly updated in the CRM. This means that customer service representatives, sales teams, and even technicians have access to a complete history of all interactions, including past service calls, equipment details, customer preferences, and communication logs.
This comprehensive view empowers the team to offer more personalized service, anticipate customer needs, and resolve issues more efficiently. For instance, a technician arriving at a job site can instantly see the customer’s equipment history and any previous issues, allowing them to diagnose problems faster and provide more informed solutions, thereby boosting customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Optimizing Stock Levels and Reducing Delays with Inventory Management Systems
Efficient inventory management is crucial for minimizing operational costs and ensuring timely service delivery. Integrating HVAC dispatch software with inventory management systems provides real-time visibility into stock levels of parts and equipment. When a technician requires a specific part for a repair, the dispatch system can check its availability in the inventory system. If the part is in stock, its quantity is automatically reduced.
If it’s low, the system can trigger an alert for reordering or even initiate an automated purchase order. This prevents costly delays caused by missing parts and avoids overstocking, which ties up capital. For example, if a common part like a capacitor is frequently used, the integration can ensure that stock levels are maintained above a predetermined threshold, preventing technicians from having to reschedule jobs due to unavailability.
Targeting Service Reminders and Promotions with Marketing Automation Tools
Linking HVAC dispatch software with marketing automation platforms opens up powerful avenues for customer engagement and proactive service. The dispatch system holds valuable data on customer service history, equipment types, and installation dates. This information can be leveraged by marketing automation tools to send highly targeted service reminders, such as annual maintenance checks, or personalized promotions based on the customer’s specific equipment.
For instance, if a customer has an older HVAC unit, the system could trigger a reminder about potential efficiency upgrades or a special offer on a new system. This proactive approach not only helps customers maintain their equipment but also generates new revenue streams for the HVAC business by fostering repeat business and upselling opportunities.
Conceptual Diagram of Information Flow
To illustrate the interconnectedness, consider the following conceptual flow:
- Customer Initiates Service Request: A customer contacts the HVAC company.
- Dispatch Software Records Request: The request is logged in the HVAC dispatch software, capturing details like customer information, issue description, and desired service time.
- CRM Update: The dispatch software automatically updates the customer’s record in the CRM with the new service request details, ensuring a unified customer view across departments.
- Technician Assignment and Job Execution: A technician is dispatched. They access job details via the dispatch software, potentially checking inventory availability for parts.
- Job Completion and Data Transfer: Upon completing the job, the technician updates the status in the dispatch software. This triggers the transfer of labor, parts, and cost data.
- Accounting Software Integration: The dispatch software sends this finalized job data to the accounting software.
- Invoice Generation and Financial Reporting: The accounting software automatically generates an invoice for the customer and updates financial records, contributing to real-time financial reporting.
- Marketing Automation Trigger: Based on the completed service date and equipment, the dispatch software can signal the marketing automation tool to schedule a follow-up reminder for future maintenance.
APIs Facilitate Interoperability in the HVAC Service Ecosystem
APIs, or Application Programming Interfaces, are the connective tissue that enables different software solutions to communicate and exchange data seamlessly. In the context of HVAC service dispatch, APIs act as intermediaries, defining the rules and protocols for how various applications can request and receive information from each other. For instance, when the dispatch software needs to retrieve customer information from a CRM, it makes an API call to the CRM.
The CRM’s API then processes this request, retrieves the relevant data, and sends it back to the dispatch software in a structured format. This eliminates the need for custom-built, one-off integrations for every single connection. APIs allow for real-time data synchronization, ensuring that all connected systems have the most current information. This is critical for tasks like inventory checks; a technician using the dispatch app can instantly see if a part is available in the inventory system because an API call has queried the inventory database.
Similarly, when a job is completed, an API can push the service details to the accounting software for immediate invoicing, or to a project management tool for internal tracking. The flexibility offered by APIs means that businesses can choose the best-of-breed applications for their specific needs and integrate them into a cohesive operational workflow, rather than being locked into a single vendor’s ecosystem.
This adaptability is crucial for HVAC businesses that are constantly evolving and seeking to leverage new technologies to improve efficiency and customer service. The development of robust and well-documented APIs by software vendors is therefore a key factor in determining the true value and long-term viability of any HVAC dispatch software solution.
Wrap-Up
In essence, HVAC dispatch software is more than just a scheduling tool; it’s a comprehensive solution that drives operational excellence and elevates customer service. From optimizing technician routes with GPS integration to empowering field staff with mobile applications and providing management with insightful data analytics, the benefits are far-reaching. By embracing these advanced digital tools, HVAC companies can navigate the complexities of service management with greater agility, ensuring timely, efficient, and high-quality service delivery that fosters customer loyalty and business growth.
FAQ Compilation
What are the key benefits of using HVAC dispatch software?
Key benefits include improved efficiency, reduced response times, enhanced technician utilization, better customer satisfaction, and streamlined administrative tasks.
Can HVAC dispatch software be customized to fit specific business needs?
Yes, most modern HVAC dispatch software offers customizable workflows, reporting, and features to adapt to the unique requirements of different HVAC businesses.
How does HVAC dispatch software handle emergency service calls?
The software typically allows for quick creation and prioritization of emergency work orders, enabling rapid technician assignment and dispatch to the site.
Is HVAC dispatch software suitable for small HVAC businesses?
Absolutely, many solutions are designed with scalability in mind and offer tiered pricing or feature sets that are cost-effective for small to medium-sized businesses.
What kind of training is typically required for HVAC dispatch software?
Training usually covers basic navigation, work order management, scheduling, and communication features for both office staff and field technicians.